Agriculture played important role in Rajasthan state because the maximum population are living in rural areas and they depends on the agriculture activity. Due to minimum rainfall the drought is the main problem for agriculture sector. The Major crops of the area are Maize and Jawar in Kharif season and Rabi seasons Wheat and Mustard.
Soil & Vegetation
The soil and vegetation of Rajasthan alters with its wide-ranging topography of the state and the availability of water. The varied kind of soils available in Rajasthan are mostly sandy, saline, alkaline and chalky (calcareous). Clay, loamy, black lava soil and nitrogenous soils are also found.
Owing the limited rainfall seasonal vegetation such as a few grass species, shrubs and dwarf trees can be found. However, food crops are grown in the plains that are drained by the rivers and streamlets owing to the alluvial and clay soil deposits. The hilly tracts of the Aravali are characterized by the black, lava soils that sustain the growth of cotton and sugarcane.
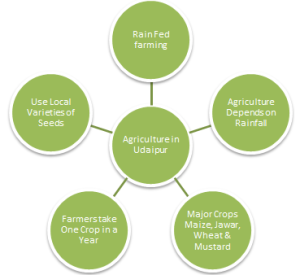
Land use and Agriculture in Udaipur
Rain fed farming is in practice. The agriculture production depends on timely and sufficient occurrence of rainfall. The Major crops of the area are Maize and Jawar in Kharif season and Rabi seasons Wheat and Mustard. Generally most of the farmer able to take only one crop in a year during Kharif season as agriculture, which is dependent on the rain. The farmers are using local varieties of seeds during sowing. The Vegetable crops like brinjal, Chilly, etc. also grown but it all depend on availability of water sources.
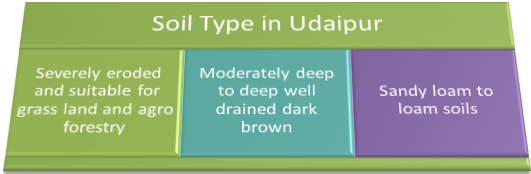
Soil type in Udaipur
The soils on hills are shallow. Well drained gravelly soil (35-60% gravels). The depth of soil is 8-10 cum. These are severely eroded and suitable for grass land and agro forestry. However the soils of pediments are moderately deep to deep well drained dark brown, sandy clay loams to clay loam soils on gently slope with slight risk of erosion. Soils along the course of rivers / streams are deep to very deep, well drained, sandy loam to loam, slightly affected with solidity. Organic and carbon contents are low. The soils on pediment could be cultivated for rain fed Kharif crops while these can be put under cropping during Rabi, with assured irrigation facilities.
Limitation in Agriculture in Rajasthan
Total cropped area in the state is 206.22lac ha. Rainfall is highly inadequate, 61% of area is in arid and semi-arid tracts where soil has poor fertility, low water holding capacity, high infiltration rate, 12lac ha area is either saline or alkaline, crops suffer from high temperature and wind effect, limited availability of grounds water, limited spread of retail outlets for agriculture input, limited power supply, lack of PHM and processing facility, low farm mechanization.
Production of Horticulture crops in states of Rajasthan
| Crops Name | Places in Rajasthan State |
| Mandarin | Warm humid areas of Jhalawar |
| Kinnow | Dry and cool climate of Ganganagar |
| Ber | Western parts of the State |
| Aonla | Central semi arid parts |
| Low volume high value seed spices crop cumin | Barmer, Jalore, Pali, Jodhpur, Nagaur, Bhilwara, Ajmer, Tonk |
| Coriander | Kota, Baran, Jhalawar, Bundi, Chittorgarh |
| Fennel | Sirohi, Tonk |
| Chilly | Jodhpur, Ajmer, Bhilwara, Tonk, S. Madhopur, Karoli |
| Garlic | Jodhpur, Chittorgarh, Baran, Jhalawar, Kota |
| Vegetables like onion, tomato, pea, okra, Cole crops, cucurbits etc | Central western parts of the state |
| Isabgol | Barmer, Jalore |
| Mehandi | Pali |
| Sonamukhi | Jodhpur, Pali |
| Ashwagandha | Nagaur, Jhalawar |
| Aloevera | Jaipur, Ajmer |
| Aromatic grasses | Baran, Ganganagar |
Horticulture
To boost up production and productivity of different horticultural crops in the state and overall development of this sector, following objectives and priorities have been identified:
- Production of quality planting material
- Promotion of sprinkler and drip irrigation system
- Promotion of high value vegetable, flower and aromatic crops.
- Organic farming of fruit, vegetable and spices
- Green house cultivation
- Promotion of water harvesting structure for irrigation in rainfed area.
- Post harvest management and marketing of horticulture produce.
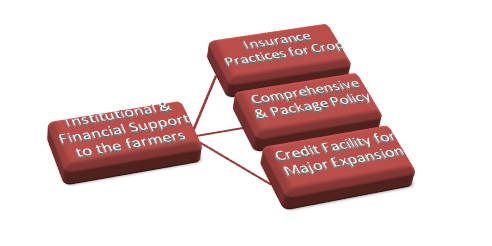
Institutional Support to farmers
- Crop insurance – better crop insurance practices are needed in Rajasthan as agriculture is rain fed and drought is regular phenomenon.
- Comprehensive policies for insuring not just crops but a package policy as is being made available in other states.
- Credit availability for agriculture – major expansion has been in urban and semi urban areas for support to agriculture or for value addition not to the cultivators.
Organic Farming
- Promotion of direct marketing by the Department of Agriculture of organic products.
- Preparation of a list of crops, herbs and livestock that can be sourced from rain fed regions in view of the international trade in organic food and allied products.
- Carry out country wide survey of areas in arid, semiarid and dry sub humid regions about the use of synthetic inputs, select crops to fetch a premium price in international markets.
- To create awareness and capacity building of farmers on cultivation, marketing, certification and harvesting.
- Develop preferential policy instruments for rain fed farmers – subsidized inputs, market information and certification.
Click on below buttons and Download PDF files for more details in this context.
